
Reshaping Business for Modern Success: The Power of Supply Chain Innovation
By: Anna Bliss Email: blis3345@vandals.uidaho.edu
Home Town: Bonners Ferry, Idaho High School: Bonners Ferry High School
Major: Accounting
Department: Business
College: College of Business and Economics
Abstract
Companies face unprecedented challenges in today’s ever-changing business landscape due to global expansion, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. As a result, businesses are adopting various supply chain and operational strategies and tactics to stay competitive, which is often demonstrated in the company’s financial performance. This research uses ten years of longitudinal firm-level data and financial performance analysis to evaluate different business model innovations.
Three industry case studies (airline, mass merchandise, and consumer electronics) provide insights into how companies adapt their operational processes, innovate in the market, and respond to consumer requests to gain a competitive advantage.
Our study highlights the necessity for businesses to embrace supply chain innovation. Business model innovation is not an option but a strategic necessity, with a focus on adaptability, sustainability, and customer-centricity.
Introduction
Various companies operating within the same industry may employ different approaches to designing, producing, and delivering their products and services, each with a unique focus. Our objective is to investigate the distinct operational processes and value propositions adopted by companies across various sectors. We seek to gain insights into their financial and operational performance and reflect on the impact of these processes.
Southwest Airlines is unique in the airline industry due to its policy of not having assigned seats. Unlike other major airlines, where passengers either choose a seat when booking their flight or pay an additional fee to be assigned to a different seat category, Southwest Airlines claims that this approach has helped them gain efficiency in their operations. In the mass merchant industry, companies such as Costco, Sears, and Amazon use completely different operational processes. Costco focuses on delivering large volumes of goods at a low price, while Sears offers more choices in their products, and Amazon provides even more choices through its online marketplace. In the consumer electronics industry, Apple and Blackberry, who used to be competitors, operate differently. We want to examine all these differences in terms of financial and operational performance to gain insights.
By leveraging financial performance data, businesses can gain invaluable insights into optimizing their supply chains. By doing so, they can create effective business models that are both efficient and sustainable. This research focuses on the intersection of supply chain management, business models, and financial analysis. It emphasizes the strategic importance of integrating all three to drive efficiency, profitability, and sustainability in modern enterprises.
Methodology
We collect financial performance data from MorningStar.com for corporations over an extended period. We then use the DuPont Model to compare the profitability, efficiency, and leverage of the company group by calculating the net profit margin, total asset turnover, and equity multiplier. These results are further used to calculate the return on assets and equity.
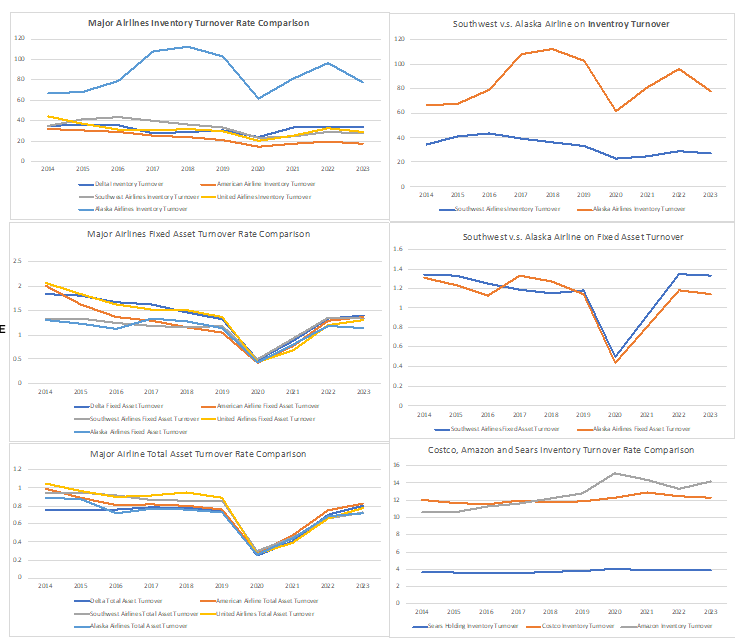
We assess the performance of companies by utilizing industry peer groups and evaluating their effectiveness in converting inventory into sales. We use performance measures such as inventory turnover ratio and total asset turnover ratio. In the airline industry, we focus on the fixed asset turnover rate because of the high value of their fixed assets such as airplanes. We have given special attention to Southwest Airlines and Alaska Airlines due to their similarity in business focus.
DuPont Model

Comparison of Industry Ratios
Supply Chain Impact on Business Models and Company Performances
Supply chain management is a critical aspect of management that brings together various functions, such as accounting, finance, and marketing, to ensure the delivery of high-value products or services to customers. It involves three or more entities, including organizations and individuals, who are directly involved in the upstream and downstream flows of products, services, finances, and/or information from a source to a customer (Mentzer et al, 2001). As market competition and business innovation continue to grow, more companies are adopting a business model framework to design and deliver their products and stay competitive. The core of a business model is the value proposition and operating model. The value proposition defines what is being offered to whom, while the operating model defines how the offerings are profitably delivered. We can conveniently map these two questions to the supply chain management domain and seek managerial insights.
Results
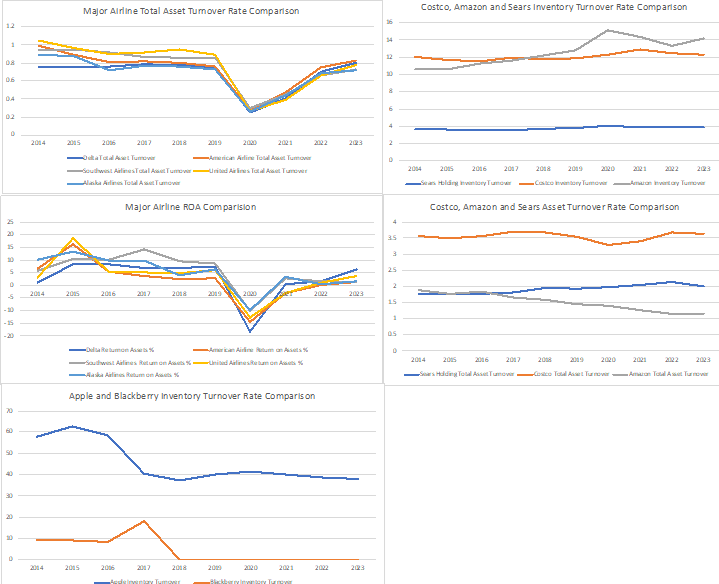
In the United States airline industry, there are five major airlines: American Airlines (with a 17.5% market share), Delta Airlines (with a 17.3% market share), Southwest Airlines (with a 16.9% market share), United Airlines (with a 15.6% market share), and Alaska Airlines (with a 6.2% market share). Despite having the smallest market share, Alaska Airlines is recognized for its efficiency and superb operational performance. This is reflected in its inventory turnover ratio, which is almost twice that of its competitors. A comparison between Alaska Airlines and Southwest Airlines, which both focus primarily on regional service, showed that Alaska Airlines outperformed Southwest in terms of inventory turnover rate and had an advantage in fixed asset turnover. However, all airlines experienced a significant decline in business and efficiency in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in near-zero values for fixed asset turnover rate, total asset turnover rate, and Return on Asset (ROA).
In the world of mass merchants, Costco and Amazon stand out as examples of operational efficiency, with excellent inventory and asset turnover rates. On the other hand, Sears is lagging at an alarmingly slow rate, with a low inventory turnover rate that is nearly seven to eight times less than that of Amazon and Costco. This explains why Sears has undergone multiple bankruptcy scenarios and is currently performing poorly. When comparing Costco and Amazon, it’s important to note that Costco uses a traditional membership-based warehouse operation, while Amazon is focused on e-commerce with almost no physical storefront. Despite this difference, their inventory turnover ratios are at a similar level. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Amazon had a more significant lead over Costco.
In the consumer appliance industry, Apple is unequivocally the market leader, thanks to its robust product ecosystem. The company’s emphasis on customer experience and ecosystem development has resulted in highly efficient operations and significant financial gains. When compared to its longtime rival, Blackberry, Apple’s performance was almost six times better during the 2014-2015 period.
Conclusion
Supply chain innovation refers to the strategic implementation of new processes, technologies, or methodologies within a company or the entire supply chain ecosystem. This is done to improve efficiency, reduce costs, increase flexibility, and gain a competitive edge. It involves continuously evolving and adapting supply chain practices to meet changing market demands, consumer preferences, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements. While companies may adopt different approaches and processes, the financial and operational results may not always meet executives’ expectations.

